How To Conduct An ISO 17025 Internal Audit
I have dedicated my career to ensuring that laboratories meet the high standards of the ISO/IEC 17025:2017 standard. I am a certified ISO/IEC 17025 assessor for one of the largest accreditation bodies in the world. In this guide, I detail a systematic approach to conducting an ISO 17025 internal audit. I also offer a free ISO 17025 internal audit checklist that you can download and use as a resource to support your audit activities.
Many laboratories struggle with the complexity of internal audits. A structured audit process not only helps in maintaining accreditation but also improves the consistency and quality of test results. The approach I describe breaks the audit into two main parts: the horizontal audit and the vertical audit. Understanding and applying these methods support the effective review of all elements of the standard.
To complement this guide, we’ve created a concise video that visually walks you through the ISO 17025 internal audit process. This video highlights key steps, best practices, and how to effectively use our free internal audit checklist. Whether you’re new to ISO 17025 or seeking to refine your audit approach, this video offers valuable insights.
Understanding the ISO 17025 Internal Audit
The ISO 17025 internal audit is very important for ensuring that your laboratory practices meet internationally recognized standards. The audit is designed to verify that both management and technical processes align with all required procedures. Fundamental to the audit is a two-part approach. One part, the horizontal audit, provides an all-in-one overview using a checklist that covers each element of the standard as required by section 8.8 of ISO/IEC 17025:2017. The second part, the vertical audit, reviews individual test or calibration methods in depth.
With my extensive experience in auditing laboratories, I have observed many challenges in managing nonconformities and maintaining audit records. I designed this guide to help laboratory managers, quality assurance teams, and technical staff better understand the process. By following these systematic steps, you can identify gaps, improve processes, and consistently meet the rigorous demands of accreditation.
🧪 Become a Certified Internal Auditor
Gain in-depth knowledge of ISO/IEC 17025:2017 standards and learn how to conduct effective internal audits within your laboratory.
- Detailed understanding of ISO/IEC 17025:2017 clauses.
- Implement ISO/IEC 17025 requirements in testing or calibration labs.
- Develop skills for auditing laboratory activities.
- Prepare essential laboratory documents like quality manuals and procedures.
ISO 17025 Internal Audit Planning and Preparation
Before beginning the audit, careful planning helps ensure that no part of the process is overlooked. Preparation involves assembling the necessary documentation, selecting auditors with the requisite knowledge, and gathering the free ISO 17025 internal audit checklist that I offer. The checklist is a practical tool for capturing data and ensuring that each clause of the standard is addressed.
The audit is divided into two parts. The horizontal audit is a table-top review that uses the checklist. It covers all of the clause elements of the standard as specified in section 8.8. On the other hand, the vertical audit requires you to trace a sample through each test method or calibration method to capture the technical requirements of the ISO/IEC 17025:2017 standard. This dual approach provides both an all-in-one overview and a detailed assessment. Keep in mind, the horizontal audit can be used as a gap analysis as well.

Conducting an ISO 17025 Horizontal Internal Audit
The horizontal audit focuses on the overall compliance with ISO 17025. The checklist I provide is designed specifically for this purpose. It captures every element of the standard as mandated by section 8.8, ensuring all clauses have been reviewed. It is a non-intrusive, table-top method that brings clarity to the broad picture.
Key Areas Addressed in the ISO 17025 Internal Horizontal Audit
The Horizontal part of the internal audit addresses the basics behind the intent of all ISO standards. In other words, ISO is all about three important elements.
- Say what you do,
- Do what you say you do.
- Show evidence that you actually have done what you say you do.
It is highly recommended that the laboratory takes the necessary time, at least once a year, to go through each and every clause element of the standard by using a checklist that has every clause and subclause element of the standard on the checklist. It is also a good idea to have a month-by-month ISO 17025 implementation timeline as well. Click on the link below, to download the free ISO 17025 internal audit checklist that I give away to see exactly what I mean.
It is recommended that you identify the associated laboratory documents in sets of three for each clause element as follows:
1. Upper-level document that says that you meet this requirement (i.e. appropriate section of the quality manual). This is the “say what you do” part.
2. Lower-level document that describes how you meet this requirement. This can be a reference to the SOP or procedure that describes how you do what you say you do. This is the “do what you say you do” part.
3. Objective evidence showing you meeting this requirement (record). This is the evidence that you have actually performed what you say you do. This is the associated record.
To fully understand what I mean, please take a look at the image below. This is a snapshot of an ISO 17025 checklist showing parts of clause 6.4 of the standard.
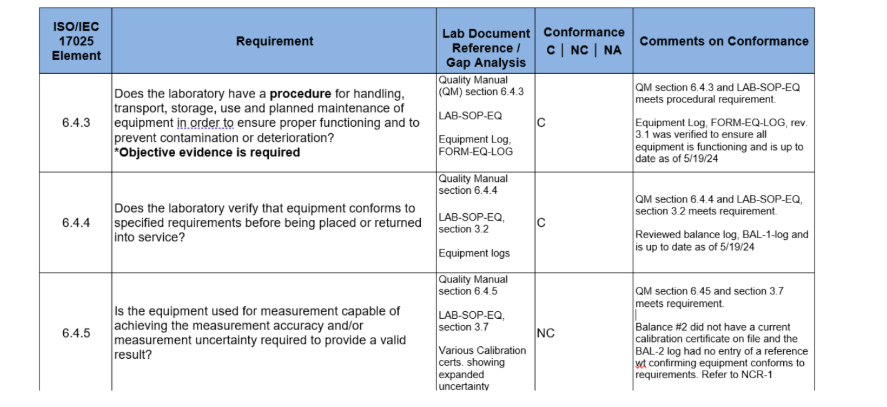
If you take a close look at the third column in the image above you will notice that all three of the above-mentioned elements are captured. For example, the first row shows that section 6.4.3, of the lab’s quality manual says that they meet section 6.4.3 of the ISO/IEC 17025 standard. This is the say what you do part. Then, LAB-SOP-EQ represents the procedure for the handling, transport, storage, use and planned maintenance of equipment. This represents the how you do what you say you do part, and the FORM-EQ-LOG, Equipment Log is the record that represents the objective evidence that the lab does what they say they do.
The idea here is that whoever fills out column three of this checklist for every clause element of the standard, will, by default, become very familiar with the labs quality management system and the ISO/IEC 17025:2017 standard. In fact, once this task is completed, it should not change from you to year, unless you completely rewrite your quality manual and procedures and change the document IDs. The only changes that will occur will be the level three documents or records. For example, calibration records expire. So a calibration record that was used in 2020, will not be current for an internal audit being conducted in 2025. This is what column 5 is used for.
So, as you can see, column 3 of this checklist can be done one time and column 5 can be done once a year during your yearly internal audit. This now serves as a part of the internal audit record that is auditable by your accreditation body.
This checklist provides a structured way to confirm that each aspect of your laboratory’s operations adheres to the standard. This process makes it easier to detect any gaps that need be escalated to your corrective action process. It can also be used as a gap analysis tool. If you find that you are missing one of the three types of documents, you know what documents you need to create or purchase templates for.
Another advantage to using this type of checklist is that you can train someone to learn and understand the laboratory’s quality management system and how it meets the requirements of the ISO/IEC 17025 standard.
Conducting a Vertical Audit
The vertical audit jumps into the technical details of each test or calibration method. Unlike the horizontal audit that looks at the broader process, the vertical audit follows a sample through each step of the test method or calibration procedure.
When you undertake the vertical audit, you must trace a sample through every technical step. For a testing laboratory, this means following the procedure for each test method. For a calibration laboratory, it involves reviewing each calibration method. This audit reviews technical procedures corresponding to clauses 6.2, 6.3, 6.4, 6.5, 7.2, 7.3, 7.4, 7.5, 7.6, 7.7, and 7.8. The process ensures the technical competence of the operations.
Steps in a Vertical Audit
- Select a representative sample from each test or calibration method.
- Trace the sample through the entire process, verifying that every documented technical requirement is followed (a simple table or checklist can be used).
- Review evidence such as calibration certificates, test records, and method validations.
- Assess compliance with technical procedures that the standard requires.
The vertical audit method provides a clear view of whether the laboratory complies with each technical criterion of the ISO 17025 standard. It is a very important step that complements the horizontal audit by ensuring that no technical detail is left unchecked.
Below is a graphical representation of a vertical audit checklist that can be used. A simple table can also be used. All you need to do is capture the appropriate sections of the standard that are considered the ISO 17025 technical requirements.
|
Clause Element |
Objective Evidence |
Compliant/Noncompliant |
|
6.2 – Personnel |
Training and competence records; staff qualification certificates; job descriptions and role competency requirements; personnel authorization list. |
C or NC |
|
6.3 – Facilities & Environment |
Environmental condition logs; facility maintenance and calibration records; cleanroom protocols; access controls |
C or NC |
|
6.4 – Equipment |
Equipment inventory; calibration and verification certificates; maintenance schedules and records; usage logbooks. |
C or NC |
|
6.5 – Metrological Traceability |
Calibration records for reference standards; certified reference materials; traceability chain documentation |
C or NC |
|
7.2 – Selection & Validation of Methods |
Documented test methods; method validation and verification reports; method selection and approval records. |
C or NC |
|
7.3 – Sampling |
Sampling procedure; sampling plans; completed sampling forms with IDs, date/time, and personnel. |
C or NC |
|
7.4 – Handling of Test/Calibration Items |
Chain-of-custody records; item labeling system; storage condition logs; disposal/return records. |
C or NC |
|
7.5 – Technical Records |
Raw data records; lab notebooks; instrument outputs; data analysis logs; record revision history. |
C or NC |
|
7.6 – Measurement Uncertainty |
Uncertainty evaluation procedures; uncertainty budget worksheets; calculation records. |
C or NC |
|
7.7 – Ensuring Validity of Results 7.8 – Reporting of Results |
Quality control charts; proficiency test results; audit reports; corrective action records. Sample test reports; report templates/checklists; reviewer approval records |
C or NC C or NC |
It is recommended that the laboratory fill out a form like this for each of the methods on their scope. In other words, for each test or calibration method.
Documenting Nonconformities and Opportunities for Improvement

After both parts of the audit are completed, the next step is to identify gaps or nonconformities. During the audit, you should record issues and potential areas for improvement on a table provided in the free checklist. It is important to capture detailed records of each nonconformity, noting the specific clauses that are not met and explaining why the gap exists.
What to Document
- Each nonconformity identified in the horizontal audit.
- Issues discovered during the vertical audit.
- Opportunities for improvement that could give a boost to overall laboratory quality.
- Supporting evidence and observations that justify the identified gaps.
All of these records become part of your internal audit documentation. Keeping clear records helps during the accreditation process and makes future audits smoother.
Escalating and Correcting Nonconformities
Once you have documented the nonconformities and opportunities for improvement, the next step is not to leave those observations as mere notes. It is important to escalate each gap into a corrective action plan. The escalation process involves assigning responsibilities, setting deadlines, and documenting what changes need to be made.
Corrective actions should be practical and achievable. They could range from revising procedures and additional staff training to upgrading equipment. Once the corrective actions are implemented, the internal audit records should be updated to reflect these efforts. This continuous process helps in maintaining compliance over time.
Steps in the Corrective Process
- Review each gap with the team responsible for that particular process.
- Agree on a timeline and responsibility for each corrective action.
- Implement the corrective actions and train staff as needed.
- Update the documentation and checklist records with the changes.
This systematic follow-up practice ensures the laboratory remains in line with the ISO 17025 requirements and continuously improves.
Finalizing and Maintaining Audit Records

Completing an audit is only part of the process. It is essential to maintain detailed records of both the horizontal and vertical audits. These records serve as evidence during external assessments and play a key role in the ongoing improvement of your laboratory’s processes.
Each step of the internal audit should be documented meticulously. This includes the audit preparation, the checklist reviews, the identification of nonconformities, the escalation of corrective actions, and the final resolution of each issue. Well-maintained records help build a history of improvements that provide confidence to accreditation bodies and internal teams alike.
Internal audits are one of the most powerful tools for maintaining ISO 17025 accreditation, but they’re just one part of the picture. If you want to see how audits, surveillance visits, reassessment, and continual improvement fit together, check out my guide on maintaining ISO 17025 accreditation
.
Frequently Asked Questions
What if I find a significant nonconformity?
If a major nonconformity is discovered, it is important to document the issue thoroughly, escalate it immediately, and assign a dedicated team member to lead the corrective action. Using the checklist, record all observations and planned actions. This approach ensures that the problem does not recur.
How often should an internal ISO 17025 audit be conducted?
Internal audits are recommended on a regular basis, such as annually or more frequently if significant changes occur in laboratory operations. Regular audits help maintain compliance and ensure improvements are continuously implemented.
Can the free ISO 17025 internal audit checklist help in future audits?
Yes, the checklist is designed to be an all-in-one tool. It helps record observations during both the horizontal and vertical audits and organizes corrective actions. Keeping past checklists can provide a valuable reference for improvements over time.
Next Steps and Additional Resources
The process of conducting an ISO 17025 internal audit may seem extensive, but breaking it down into systematic parts makes it much more manageable. Begin by downloading my free ISO 17025 internal audit checklist. This resource assists in both planning and documentation while guiding you step by step through the audit process.
Start by conducting the horizontal audit to review all the clause elements with your checklist. Then, follow up with the vertical audit to trace samples through their respective test or calibration methods. Carefully document any gaps, and work with your team to escalate these issues into corrective actions. By ensuring every step is recorded, you maintain a clear audit trail that supports your laboratory’s ongoing compliance and improvement.
Maintaining a thorough internal audit process not only supports external accreditation but also gives a boost to your laboratory’s overall performance. A robust system of record-keeping and corrective action tracking leads to better lab practices and increased confidence among stakeholders.
What remains very important is a commitment to maintaining these auditing practices over time. Keeping your records updated and revisiting the process periodically ensures continuous improvement and preparedness for any external audits or assessments.
If you have any further questions about conducting the internal audit or need guidance on implementing corrective actions, the resources provided in this guide serve as a starting point to understanding and applying ISO 17025 standards consistently.
Additional Best Practices for Sustained Lab Excellence
Implementing a robust internal audit process is not just about meeting accreditation requirements. It is also about increasing efficiency and ensuring that laboratory operations run smoothly. It is very important to have regular training sessions, encourage open dialogue among team members, and make measured improvements when necessary. By scheduling periodic refresher audits and reviewing updated documentation, laboratories ensure that even minor issues are recognized and addressed. Every team member plays a vital role in fostering an environment where quality and precision are top priorities.
Moreover, maintaining clear communication between all levels of the laboratory staff is critical. When audits reveal areas in need of improvement, holding review meetings to discuss these findings helps in setting out actionable items. For instance, when changes are needed in a particular process, the team can come together to map out the necessary steps to achieve compliance. This collaborative effort not only boosts overall performance but also cultivates a sense of ownership and responsibility among personnel. Regular discussions lead to feedback that can further refine audit methods, making the process more efficient over time.
In addition, investing in digital audit tools and modern record-keeping methods can ease the administrative burden significantly. Digital platforms allow for quicker access to documented evidence and smooth revisions. Using cloud-based systems, staff can update records in real time, ensuring that every audit reflects the most current state of operations. This approach not only speeds up the resolution of issues but also makes it easier to monitor progress over time. When your audit process is dynamic and intertwined with technology, it becomes simpler to pinpoint areas that need extra focus, thereby contributing to both immediate gains and long-term quality improvements.
Laboratories that adopt these best practices are better positioned to handle changes and challenges. The combination of regular staff training, open communication, and advanced audit tools creates an atmosphere where continuous improvement is not just encouraged but is part of the everyday workflow. By working together and staying proactive, your laboratory can consistently meet and exceed quality standards while also preparing for future industry demands.
🕒 Book Your Free 45-Minute Consultation
Have questions about ISO/IEC 17025 or ISO 9001 implementation or accreditation? Schedule a free 45-minute consultation with me to discuss your Company or laboratory’s needs and how we can achieve compliance together.
Schedule Your Consultation





